
At alltasksIT, we’ve had the privilege of conducting security audits for leading Australian brands. During these assessments, we engaged with our customers to gather direct feedback on what they thought of the process end to end. We ask them: What did you appreciate from the assessment? Did we meet your expectations? Did our services add business value? Would you choose us again?
At alltasksIT, our customers trust us for expert advice and practical steps towards technology best practices. To uphold our reputation, we put ourselves in our customers’ shoes when approaching security assessments. We ask: How would we want a security audit presented if we owned the brands we serve? Is our approach not only industry-aligned but also uniquely valuable to our customers? The answer came down to the six things alltasksIT regularly talks about when we talk security. They are-
In reality, there’s much more you can do to protect your business, and alltasksIT is here to help. This article will be the first of many to come offering practical, real-world, non-technical advice to those that need it.
We also have a special offer for those wanting to understand their security posture. Read on.
In today’s hyper-connected world, every business—regardless of size or industry—is a target for cybercriminals. The stakes are higher than ever. If you’re not actively managing cybersecurity within your organisation, directly or through a service provider, you risk being negligent. As a company owner, you could be personally liable. Your business can be fined, and so can you. For IT managers, this article provides the tools to educate your business leaders about the risks of inaction.
The Legal Landscape: Understanding Your Obligations
Australia’s Notifiable Data Breach (NDB) Scheme, governed by the Office of the Australian Information Commissioner (OAIC), mandates that businesses must notify individuals and the OAIC when a data breach is likely to result in serious harm. The penalties for non-compliance are severe, with fines in the tens of millions for companies and now, company directors. This regulatory landscape is non-negotiable; understanding your obligations under the NDB Scheme and adhering to the Essential8 mitigation strategies recommended by the Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) is critical for legal and operational resilience.
Why Modern Businesses Need to Care About Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity isn’t just an IT issue—it’s a fundamental business concern. The average cost of a data breach in Australia is $3.35 million, according to IBM’s 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report. Beyond the financial hit, a breach can damage your brand’s reputation and customer trust. But more than that, ignoring cybersecurity breaches the implicit contract between your business and customers. They trust you to protect their data; failing to do so is not just bad business—it’s negligent.

Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are particularly vulnerable to cyber-attacks, with 43% of all cyber-attacks targeting small businesses. Cybercriminals know that these businesses often lack the robust security measures of larger enterprises, making them easy targets.
Here are some of the most pressing threats:
Cybercriminals use scam messages to trick employees into divulging sensitive information, sending money, or clicking on malicious links. Phishing attacks, in particular, are a major concern, as they often lead to compromised account passwords and the hijacking of social media or other business accounts. A staggering 91% of cyber-attacks start with a phishing email.
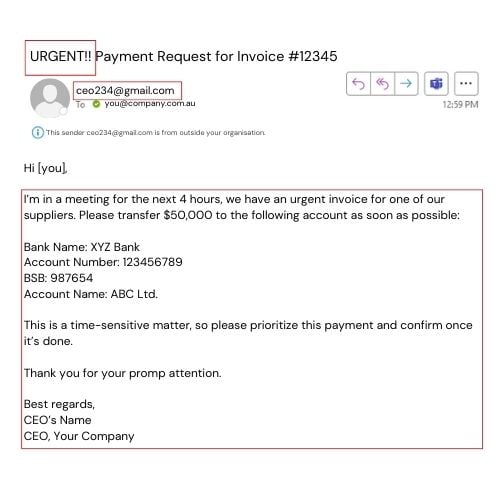
BEC attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated. Cybercriminals impersonate company executives or trusted partners to trick employees into transferring funds or sharing confidential information. In Australia, businesses have lost over $142 million to BEC scams in 2023 alone.
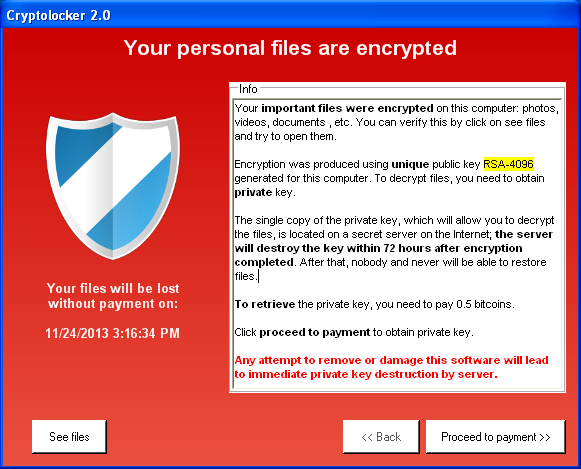
Ransomware remains one of the most destructive forms of cyber-attack. It works by encrypting your files and demanding a ransom to restore access. The ACSC reported that ransomware incidents increased by 60% in 2023, with many small businesses being unable to recover their data due to inadequate backups.
Malware, which includes viruses, spyware, and trojans, is designed to cause harm by stealing or locking your files, spying on your computer, or taking control of your systems. With remote work becoming the norm, the risk of malware infections has skyrocketed as employees connect to corporate networks from unsecured home environments.

While cyber insurance can provide a financial safety net in a cyber-attack, it is not a substitute for robust cybersecurity measures. Many cyber insurance policies contain clauses that invalidate coverage if the policyholder fails to implement basic security controls.
For example, your insurer might refuse to pay out if your business suffers a data breach due to a failure to patch known vulnerabilities or implement multi-factor authentication (MFA). This leaves your business vulnerable to the attack and without the financial support needed to recover.
Additionally, insurers are becoming more stringent in their requirements, often demanding that businesses adhere to frameworks like the Essential8. If your business cannot demonstrate compliance with these standards, you may find it difficult to obtain cyber insurance in the first place—or the premiums could be prohibitively expensive.

Protecting your business from cyber threats involves more than just buying the right software. It requires a holistic approach that includes both technological and human elements. Here’s how you can fortify your defences:
Start by understanding what your cyber insurance policy covers and what it doesn’t. Ensure that you meet all the conditions outlined by your insurer, such as implementing MFA, maintaining up-to-date software, and conducting regular security audits.
Email remains the most common vector for cyber-attacks. Implementing strong email security measures, such as those offered by Barracuda, is essential. On the other hand, an email archiver helps ensure that all communications are stored securely and can be retrieved when needed, especially during legal disputes or compliance audits.
Your employees are your first line of defence. Regular training and testing ensure they remain vigilant against phishing attempts and other scams. The Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) offers resources to help your staff identify and respond to potential threats.
A password manager helps your team create and store strong, unique passwords for each account, reducing the risk of unauthorised access. Coupled with application control—allowing only approved applications to run—you add an extra layer of security that’s hard for attackers to bypass.
Regularly scanning your systems for vulnerabilities and promptly applying patches is non-negotiable. Cybercriminals are quick to exploit known software weaknesses, so you must be quicker in closing those gaps.
With more employees working remotely, securing devices outside the office is critical. Implementing DNS filtering, which blocks access to malicious websites, can protect your business data even when employees use home internet or mobile services.
Implementing security tools is just the beginning. The real challenge lies in effectively managing them over time. Here’s how you can ensure your cybersecurity tools are working for you:
Security isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it task. Regular audits ensure that your tools are working as intended, that no critical updates have been missed, and that your systems remain secure.
Have a plan for when things go wrong. Ensure your team knows exactly what to do in a breach. Speed and efficiency can distinguish between a minor incident and a major disaster.
Cyber threats evolve rapidly, and so must your defences. Regularly update your security policies and inform your team of the latest threats and best practices.
At our Australian MSP, we believe in delivering results. We offer three tailored security assessments: Inside Threats, Outside Threats, and Data Usage. Here’s our promise: if we don’t find anything during our assessment, you don’t pay. It’s that simple.
We have a one-time offer for new customers with an existing MSP: choose one of our three assessments and pay just $2,500—valued at $7,500. Let us show you what you’re missing.
Cybersecurity is not just about technology; it’s about protecting your business and customers. Please don’t wait until it’s too late. Contact us today and take the first step towards securing your business’s future.

Chief Customer Officer (CIO)
Mark Boyd is a Chief Customer Officer (CCO), plays a key executive role responsible for overseeing the entire customer experience within alltasksIT. The CCO serves as the voice of the customer at the highest levels of the company, ensuring that customer-centric strategies are developed and implemented across all departments.